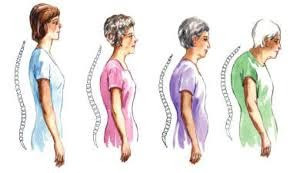
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disease that decreases bone mass and deteriorates bone tissue that leads to an increased risk of bone fragility and fracture, especially in the hip, spine, and wrist.
The American College of Physicians (ACP) recommends in an evidence-based clinic that physicians should treat women with osteoporosis with bisphosphonates (alendronate, risedronate, or zoledronic acid) or denosumab, a biologic agent.
The evidence suggests that physicians should treat women with osteoporosis with drug therapy for five years.
Continuing treatment after five years may be appropriate after reassessing the risks and benefits of continuing therapy.
ACP recommends that physicians should offer drug treatment with bisphosphonates to reduce the risk for vertebral fracture in men with osteoporosis.