Current HIV treatments need to be taken for life by those infected as antiretroviral therapy is unable to eliminate viral reservoirs lurking in immune cells. Institut Pasteur scientists have identified the characteristics of CD4 T lymphocytes that are preferentially infected by the virus — it is their metabolic (or energy-producing) activity that enables the virus to multiply. Thanks to metabolic activity inhibitors, the researchers have managed to destroy these infected cells, or “reservoirs,” ex vivo. Their findings were published in the journal Cell Metabolism on December 20, 2018.
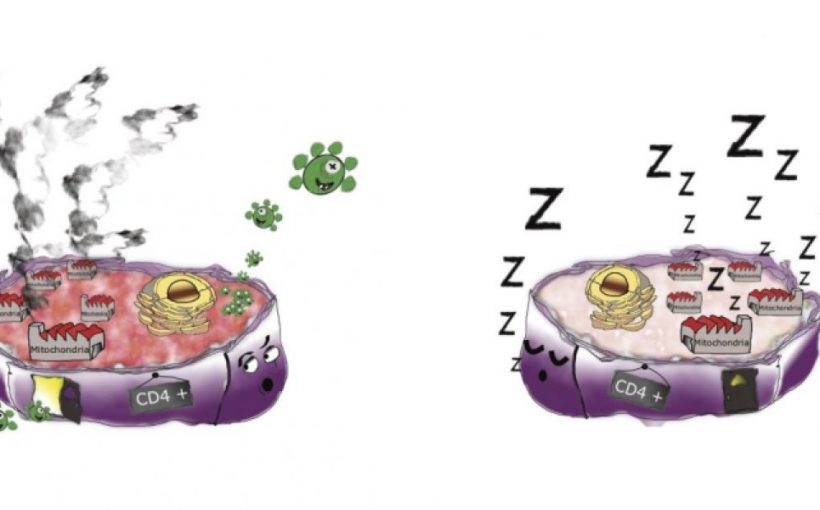
The antiretroviral treatment used today is designed to block HIV infection but it is not able to eliminate the virus from the body. The virus remains in reservoirs — the CD4 T lymphocyte immune cells, the main targets of HIV. However, the virus does not infect all types of CD4 cell and until now the reason for this was not well known. In this study, scientists from the HIV, Inflammation and Persistence Unit at the Institut Pasteur and colleagues have identified the characteristics of the different CD4 subpopulations, which are associated with HIV infection.
The more the CD4 cells are differentiated, or experienced, the more they need to produce energy to perform their function. Experiments have shown that it is the metabolic activity of the cell, and in particular its glucose consumption, that plays a key role in susceptibility to HIV infection. The virus primarily targets cells with high metabolic activity. To multiply, it hijacks the energy and products provided by the cell.
This requirement constitutes a weakness for the virus and could be exploited to tackle infected cells. Scientists succeeded in blocking the infection ex vivo thanks to metabolic activity inhibitors that have already been investigated in cancer research.
“We have observed ex vivo that, thanks to certain metabolic inhibitors, the virus is no longer able to infect cells and amplification is halted in reservoirs of patients receiving antiretroviral treatment.”
Story Source:
Materials provided by Institut Pasteur. Note: Content may be edited for style and length.