Researchers at the National Institute for Physiological Sciences in Okazaki identify the neural pathways that cause hunger-induced increases in the preference for sweet foods and the decreased sensitivity to aversive tastes in mice

Okazaki, Japan – Why does everything taste better when we’re hungry? According to new findings from the National Institute for Physiological Sciences in Japan, not only does food taste sweeter when our stomachs are rumbling, but bitter food also becomes less difficult to eat–and both effects are moderated by a neural circuit in the hypothalamus.
Generally, we prefer sweet tastes because they signal calorie-rich food, and avoid bitter and sour tastes because they signal spoiled food. However, these preferences are modified by internal states such as hunger. In a study published in Nature Communications last week, researchers found that starved mice had a greater preference for sweetness and a decreased sensitivity to aversive tastes. The research team focused on Agouti-related peptide (AgRP)-expressing neurons, which are known to be activated during hunger states to trigger feeding behavior, and identified two neural pathways that underlie hunger-induced changes in taste preferences.
“AgRP-expressing neurons are found in the hypothalamus, which is a brain region that plays a vital role in appetite regulation,” says first author Ou Fu. “We selectively activated these AgRP-expressing neurons in mice using chemogenetic and optogenetic techniques to see whether they influence the perception of tastes observed under fasting conditions.”
Optogenetic and chemogenetic techniques are popular methods for studying neuronal activity because they can manipulate neural activity very precisely. Optogenetics introduces light-sensitive agents into target neurons, whose activity can then be manipulated by light, and chemogenetics introduces designer receptors to affect the target neurons’ activity by their specific synthetic ligands.
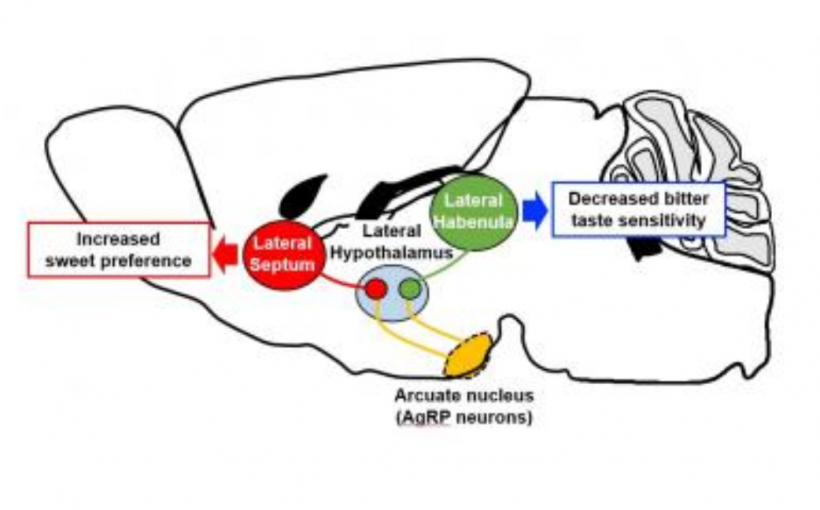
After AgRP-expressing neuron activation, downstream glutamate neurons in the lateral hypothalamus in turn modulated mice’s taste preferences via two different pathways. Glutamate neurons projecting to the lateral septum increased the preference for sweet tastes, and those projecting to the lateral habenula decreased the sensitivity to bitter tastes.
“The next steps will be to investigate whether these hypothalamic neuronal pathways are altered in pathophysiological conditions such as diabetes and obesity,” says Yasuhiko Minokoshi, co-author of the study. “For example, we already know that people with obesity have a strong preference for sweetness; this might be associated with a change in the activity of the glutamate neurons projecting to the lateral septum.”
These new findings could therefore provide the groundwork for the future development of methods to control taste preferences, which would have significant health benefits. However, much work remains to be done before this becomes a reality.