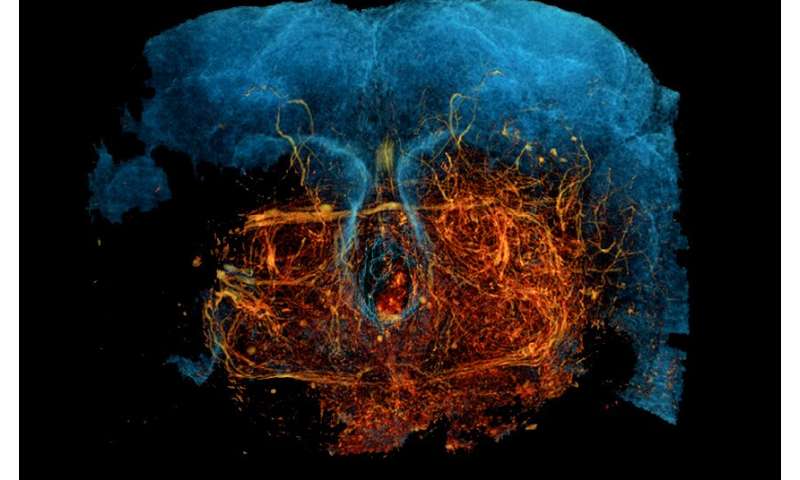
One of the grand quests in neuroscience is to build a precise map of the brain, charting all its neurons and the connections between them. Such a wiring diagram, called a connectome, promises to help shed light on how a collection of cells can together give rise to thoughts, memories, behaviors and myriad other functions.
Now, researchers at Harvard Medical School, Boston Children’s Hospital and the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) have demonstrated that a new X-ray microscopy technique could help accelerate efforts to map neural circuits and ultimately the brain itself.
Reporting in Nature Neuroscience on Sept. 14, the team describes how X-ray holographic nano-tomography (XNH) can be used to image relatively large volumes of mouse brain and fruit fly nervous tissue at high resolutions.
Combined with artificial intelligence-driven image analysis, they reconstructed dense neural circuits in 3-D, comprehensively cataloging neurons and even tracing individual neurons from muscles to the central nervous system in fruit flies.
“We think this is going to open new avenues for understanding the brain, both in how it’s organized and the circuitry that underlies its function,” said co-corresponding author Wei-Chung Allen Lee, HMS assistant professor of neurology at Boston Children’s. “This type of knowledge can give us foundational insights into neurological disorders, diseases that affect the structure of the brain and much more.”
For biological questions like neural circuit discovery, X-ray microscopy holds several advantages over current approaches based on electron microscopy (EM), according to the authors.
“We think XNH can bring a lot of value to neuroscience, because we can now access much larger volumes in shorter times,” said co-corresponding author Alexandra Pacureanu, a scientist at the ESRF. “This is the beginning of a new approach for efforts to map neural circuits.”
Near-light speed
Studying the connectome is a monumental challenge. The human brain, for example, contains some 100 billion neurons with 100 trillion neural connections, roughly the number of stars within 1,000 galaxies.
In animal models, scientists have made remarkable progress, such as imaging an entire fruit fly brain, primarily by taking serial slices of a brain, each a thousand times thinner than a human hair, imaging the slices with EM and stitching the images together for analysis.
The costs of this method can be prohibitive in terms of time and resources, requiring large numbers of EM images, which have a narrow field of view, and an intense effort to reconstruct even small neural circuits. There is a need for new imaging modalities to accelerate such efforts, the study authors said.
To do so, Lee’s lab, which studies the organization and function of neural circuits, collaborated with Pacureanu, who specializes in X-ray microscopy and neuroimaging. Spearheaded by co-first authors Aaron Kuan, research fellow in neurobiology at HMS, and Jasper Phelps, graduate student in the Harvard Program in Neuroscience, the team focused on applying XNH to neural tissue.
The technique works analogously to a CT scan, which uses a rotating X-ray to create serial cross-sectional images of a body. In contrast, XNH exposes a rotating tissue sample to high-energy x-rays at the ESRF’s synchrotron, which accelerates electrons to near-light speed around an 844-meter ring.
Unlike standard X-ray imaging, which relies on differences in X-ray attenuation as the beam passes through a tissue, XNH creates images based on variations of subtle phase shifts of the beam induced by the sample. This latter approach increases sensitivity and, combined with imaging in cryogenic conditions, helps preserve and protect the specimen from being damaged by X-ray energy.
Images generated by XNH must be interpreted to identify which structures are neurons. The team tackled this by applying deep learning, an artificial intelligence technique increasingly used for applications such as face or object recognition.
As proof of principle, the researchers scanned millimeter-sized volumes of mouse and fruit fly neural tissue and reconstructed 3-D images, achieving resolutions around 87 nanometers. This was enough to comprehensively visualize neurons and trace individual neurites, the projections from neurons that form the wiring of neural circuits.
Importantly, these reconstructions took a few days to achieve, compared to the months to years it can take to reconstruct similar volumes using serial EM sections.
Form to function
In the mouse brain, the team looked at an area of the cortex involved in integrating sensory stimuli and perceptual decision making. Previous EM studies have noted interesting structural characteristics of so-called pyramidal neurons in this area, but have been limited to sample sizes of around 20 neurons per dataset due to limitations in field of view.
Using XNH, the researchers scanned over 3,200 cells in this area. Combined with aligned EM data, the team characterized the structure and connectivity of hundreds of pyramidal neurons, which revealed distinct structural properties—such as strong and spatially compressed inhibitory inputs on certain neurite areas—that suggest unique and previously undescribed functional properties.
“Being able to visualize neurons helps us to understand the organizational principles of the brain and how different circuits or networks can perform computations that are required for behavior,” said Lee, who is an investigator at the Kirby Neurobiology Center at Boston Children’s. “We can then do further experiments to link structural data with functional experiments to try to address this question directly.”
They also imaged the neurons contained within a fruit fly leg, a structure difficult to section and study with EM. With XNH, they were able to map all of the motor neurons extending from the fly equivalent of a spinal cord into a leg, as well as the sensory neurons that relay signals to the central nervous system.
“This technique has been applied to neural tissue before, but never with this level of quality and resolution,” said Pacureanu, who is a former a visiting scientist in the Department of Neurobiology in the Blavatnik Institute at HMS. “We’ve shown that we can achieve sufficient resolution to trace neurites and move studies toward the direction of connectomes.”
The researchers are now working to improve and further optimize XNH for imaging biological tissue.
The current resolution achieved by the technique is not yet high enough to visualize synapses, which currently requires aligned EM data to study. However, the physical limits of the technique are far from being reached, the authors said, and efforts to push the resolution will be aided by a next-generation X-ray source recently operational at the ESRF.
“X-ray microscopy has particular strengths and one of our goals is to apply it to larger networks of neural connections at higher resolutions,” Lee said. “The hope is we could someday help address questions like can we understand neural circuits that underlie complex behaviors like decision making? Can we get inspiration for more efficient computer algorithms and artificial intelligence? Can we reverse engineer the algorithms of the brain?”
Additional authors on the study include Logan Thomas, Tri Nguyen, Julie Han, Chiao-Lin Chen, Anthony Azevedo, John Tuthill, Jan Funke and Peter Cloetens.
Kevin Jiang, Harvard Medical School

