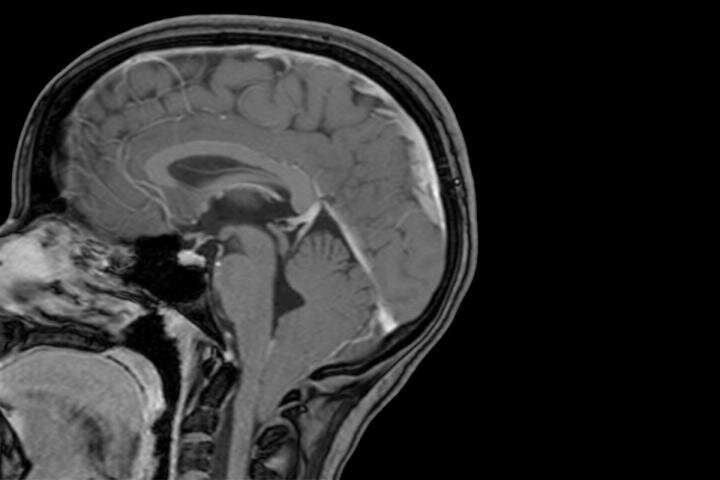
About one in 100 children has a common brain disorder called Chiari 1 malformation, but most of the time such children grow up normally and no one suspects a problem. But in about one in 10 of those children, the condition causes headaches, neck pain, hearing, vision and balance disturbances, or other neurological symptoms.
In some cases, the disorder may run in families, but scientists have understood little about the genetic alterations that contribute to the condition. In new research, scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have shown that Chiari 1 malformation can be caused by variations in two genes involved in brain development.
The condition occurs when the lowest parts of the brain are found below the base of the skull. The study also revealed that children with unusually large heads are four times more likely to be diagnosed with Chiari 1 malformation than their peers with normal head circumference.
The findings, published Dec. 21 in the American Journal of Human Genetics, could lead to new ways to identify people at risk of developing Chiari 1 malformation before the most serious symptoms arise. It also sheds light on the development of the common but poorly understood condition.
“A lot of times people have recurrent headaches, but they don’t realize a Chiari malformation is the cause of their headaches,” Haller said. “And even if they do, not everyone is willing to have brain surgery to fix it. We need better treatments, and the first step to better treatments is a better understanding of the underlying causes.”
If people start experiencing severe symptoms like chronic headaches, pain, abnormal sensations or loss of sensation, or weakness, the malformation is treated with surgery to decompress the Chiari malformation.
“There’s an increased risk for Chiari malformations within families, which suggests a genetic underpinning, but nobody had really identified a causal gene,” said senior author Gabriel Haller, Ph.D., an assistant professor of neurosurgery, of neurology and of genetics. “We were able to identify two causal genes, and we also discovered that people with Chiari have larger head circumference than expected. It’s a significant factor, and easy to measure. If you have a child with an enlarged head, it might be worth checking with your pediatrician.”
To identify genes that cause Chiari 1 malformation, Haller and colleagues sequenced all the genes of 668 people with the condition, as well as 232 of their relatives. Of these relatives, 76 also had Chiari 1 malformation and 156 were unaffected. The research team included first author Brooke Sadler, Ph.D., an instructor in pediatrics, and co-authors David D. Limbrick, Jr., MD, Ph.D., a professor of neurosurgery and director of the Division of Pediatric Neurosurgery, and Christina Gurnett, MD, Ph.D., a professor of neurology and director of the Division of Pediatric and Developmental Neurology, among others.
Sequencing revealed that people with Chiari 1 malformation were significantly more likely to carry mutations in a family of genes known as chromodomain genes. Several of the mutations were de novo, meaning the mutation had occurred in the affected person during fetal development and was not present in his or her relatives. In particular, the chromodomain genes CHD3 and CHD8 included numerous variants associated with the malformation.
Further experiments in tiny, transparent zebrafish showed that the gene CHD8 is involved in regulating brain size. When the researchers inactivated one copy of the fish’s chd8 gene, the animals developed unusually large brains, with no change in their overall body size.
Chromodomain genes help control access to long stretches of DNA, thereby regulating expression of whole sets of genes. Since appropriate gene expression is crucial for normal brain development, variations in chromodomain genes have been linked to neurodevelopmental conditions such as autism spectrum disorders, developmental delays, and unusually large or small heads.
“It’s not well known how chromodomain genes function since they have such a wide scope of activity and they are affecting so many things at once,” Haller said. “But they are very intriguing candidates for molecular studies, to understand how specific mutations lead to autism or developmental delay or, as in many of our Chiari patients, just to increased brain size without cognitive or intellectual symptoms. We’d like to figure out the effects of each of these mutations so that in the future, if we know a child has a specific mutation, we’ll be able to predict whether that variant is going to have a harmful effect and what kind.”
The association between chromodomain genes and head size inspired Haller and colleagues to measure the heads of children with Chiari malformations, comparing them to age-matched controls and to population averages provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Children with Chiari tended to have larger than average heads. Those children with the largest heads—bigger than 95% of children of the same age—were four times more likely to be diagnosed with the malformation.
The findings suggest that children with larger heads or people with other neurodevelopmental disorders linked to chromodomain genes may benefit from screening for Chiari malformation.
“A lot of kids that have autism or developmental disorders associated with chromodomain genes may have undiscovered Chiari malformations,” Haller said. “The only treatment right now is surgery. Discovering the condition early would allow us to watch, knowing the potential for serious symptoms is there, and perform that surgery as soon as it’s necessary.”
Tamara Bhandari, Washington University School of Medicine

