Google Inc. and researchers at Harvard University have teamed up to create the most detailed image of a small piece of the human brain ever produced. Google has posted an outline of the work on its Google AI Blog.
Last year, Google released what it described as a connectome of one half of a fruit fly brain. Using it, researchers and laypeople alike could browse the intricacies of the tiny fly brain. In this new effort, the team at Google has gone a step further by doing the same with a very small bit of the human brain.
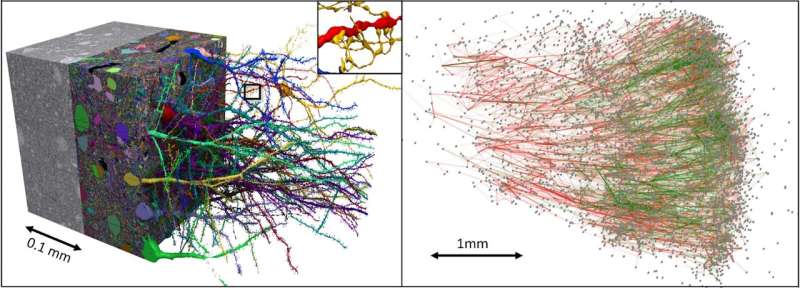
The work began by obtaining human brain tissue taken from the cortex of an epileptic patient undergoing brain surgery as part of their treatment. The tissue was then sliced into approximately 5,300 individual 30 nm sections. Each of the slices were then imaged using an electron microscope. The imaging process resulted in the creation of 225 million 2D images. A computer was then used to stitch the images together to create a 3D representation of the original brain tissue.
Next, the researchers used machine-learning algorithms to create 3D segmentations representing individual cells. Another algorithm was used to characterize 130 million synapses, which were broken down into sub-compartments. Doing so allowed for labeling structures of interest such as cilia and myelin. Human experts reviewed 100 of the cells as a means of proofreading the work by the computers. The result is what the team describes as the most detailed map ever created of connections in the human brain. The researchers refer to it as the “H01” dataset.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=bvlSV_6wKO4%3Fcolor%3Dwhite
The team has made the brain map freely available online with their Neuroglancer browser interface. It currently has information for approximately 50,000 cells, shown in 3D. More will be added soon. The cells are connected by hundreds of millions of tendrils comprising approximately 130 million synapses. The data for the project currently amounts to 1.4 petabytes.
The team at Google says that their goal in creating such tools is to provide resources for the study of the human brain using new kinds of technology.
Bob Yirka , Medical Xpress

