Studies have shown that death by suicide can increase during infectious disease epidemics. While increased community cohesion and mutual support may have initially decreased suicide risk during the COVID-19 pandemic, few studies have been conducted on the long-term impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in Japan.
A joint study by researchers at Hokkaido University and Asahikawa Medical University has analyzed trends in monthly suicide rates by age and gender from January 2016 to December 2021 in Japan using provisional mortality data in an interrupted time series analysis.
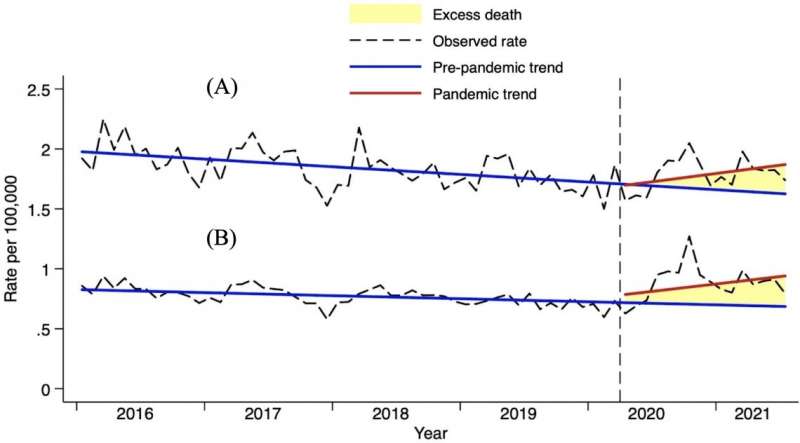
The group found that there were 1,208 excess suicide deaths for men and 1,825 for women between April 2020 and December 2021. While there was no statistically significant increase in overall suicide rates for men and women during the pandemic period, sub-group analyses revealed that there was a statistically significant increase in men aged 20–29 years and 40–49 years, and in women 20–29 years, 30–39 years, 50–59 years, 60–69 years and 70–79 years.
“Our results show that the COVID-19 pandemic has had a negative impact on trends in suicide rates in Japan, specifically in women and in younger age groups,” said Dr. Sharon Hanley, one of the study co-authors. “This indicates that governments and other agencies need to identify and provide appropriate additional support to socio-economically vulnerable subgroups of the population during the pandemic.”
Associate Professor Eiji Yoshioka who led the study said, “Since the COVID-19 pandemic is still evolving, continued vigilance and close monitoring of suicide mortality rates as well as the mental health of the population remains a priority.”
Hokkaido University

